Crawl Budget Optimisation: How to Help Google Discover & Rank Your Pages Faster
Search engines don’t have unlimited resources to crawl every page on the web. That limitation is known as crawl budget.
Understanding crawl budget SEO helps ensure Google discovers, crawls, and evaluates your most important pages-especially on large, ecommerce, or fast-growing websites.
This guide explains crawl budget optimisation in simple terms and shows how to help Google crawl your website faster.
What Is Crawl Budget?
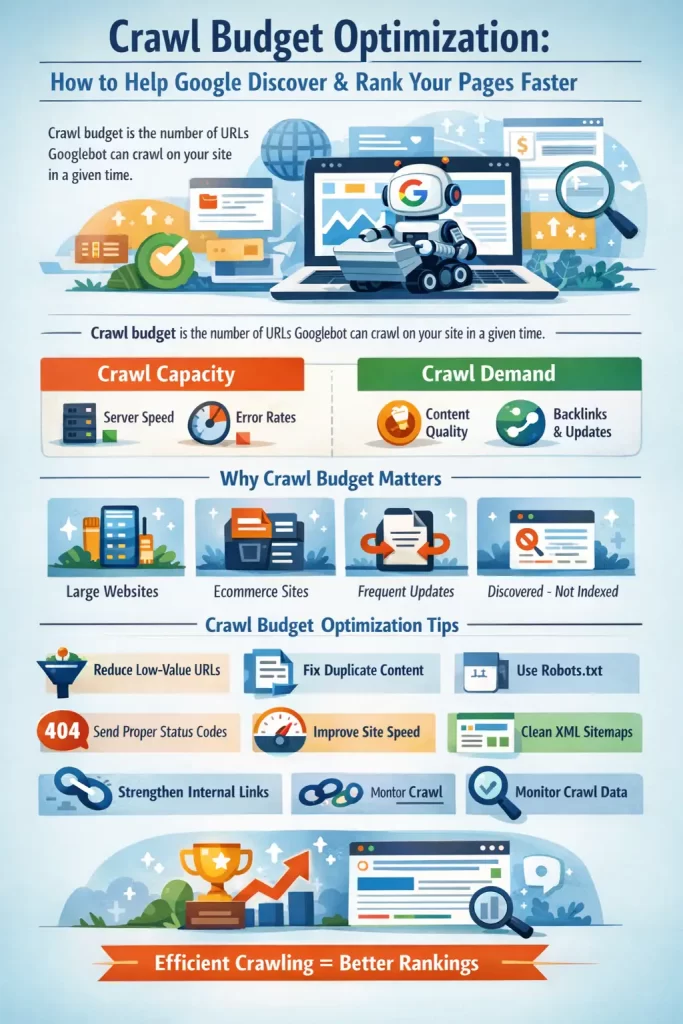
Crawl budget is the number of URLs Googlebot is willing and able to crawl on your website within a given time period.
In simple terms:
- Google visits your site
- It decides how many pages it can crawl safely
- It prioritises which URLs to crawl again
Crawling always comes before indexing and ranking. If a page isn’t crawled, it can’t rank.
When your site has more URLs than Google is willing to crawl, some pages may remain undiscovered or unindexed.
Why Is Crawl Budget Important for SEO?
Crawl budget becomes important when:
- Your site has 10,000+ pages
- You run an ecommerce site with filters and variants
- You frequently publish or update content
- Search Console shows “Discovered – currently not indexed”
If Google doesn’t crawl a page, it can’t evaluate it-and if it can’t evaluate it, it won’t rank.
Effective crawl budget optimisation helps with:
- Faster indexing of new pages
- Faster re-crawling of updated pages
- Better visibility for priority URLs
Small websites rarely face crawl budget issues, but large and complex sites often do.
How Google Determines Crawl Budget
Google crawl budget is based on two main factors.
1. Crawl Capacity (How Much Google Can Crawl)
Googlebot limits crawling to avoid overloading your server. It looks at:
- Server response time
- Error rates (5xx, timeouts)
- Overall site stability
Fast, stable servers allow more crawling. Slow or error-prone sites reduce crawl capacity.
2. Crawl Demand (How Much Google Wants to Crawl)
Even if your server is strong, Google only crawls URLs it finds valuable. Demand depends on:
- Content quality and uniqueness
- Internal and external links
- Update frequency
- Overall site popularity
Crawl capacity + crawl demand = your Google crawl budget.
Crawl Budget Optimisation: Core Principles
The aim of crawl budget optimisation is to help Googlebot spend its limited crawl resources on your most important pages, instead of wasting time on low-value or duplicate URLs.
1. Reduce Low-Value and Unnecessary URLs
Google will attempt to crawl every URL it discovers, even if that page has no SEO value.
Examples of low-value URLs:
- Filter and sort parameters
- Session-based URLs
- Internal search result pages
- Infinite pagination
Why this matters:
These URLs consume crawl budget without helping rankings. Removing or blocking them allows Google to focus on important pages.
2. Eliminate Duplicate Content
Multiple URLs serving the same content force Google to crawl each version before choosing one.
Common causes:
- HTTP vs HTTPS
- www vs non-www
- Category and tag duplicates
- Product variants with the same content
Best practice:
Use canonical tags and consistent URL structures so Google crawls fewer, clearer URLs.
3. Guide Crawlers with robots.txt
robots.txt helps control where Googlebot should and shouldn’t crawl.
Use it to block:
- Faceted navigation
- Cart, checkout, and login pages
- Calendar or infinite scroll URLs
Key principle:
Block only URLs that never need indexing. Incorrect blocking can remove important pages from search.
4. Send Clear Status Code Signals
Google remembers URLs for a long time, so proper status codes matter.
Best practices:
- Use 404 or 410 for permanently removed pages
- Avoid “soft 404s” that return 200 status
- Keep redirects short and clean
Why this matters:
Clear signals stop Google from repeatedly crawling dead or useless URLs.
5. Improve Site Speed and Server Performance
Crawl capacity is limited by how fast and stable your server is.
Slow sites:
- Reduce pages crawled per day
- Increase crawl delays
Optimisation actions:
- Improve server response time
- Reduce heavy scripts and unused CSS
- Avoid loading unnecessary assets
Faster sites allow deeper and more frequent crawling.
6. Keep XML Sitemaps Clean
Sitemaps guide Google toward important URLs.
Best practices:
- Include only canonical and indexable pages
- Update <lastmod> only when content truly changes
- Remove redirected, blocked, or deleted URLs
Clean sitemaps help Google prioritise crawling correctly.
7. Strengthen Internal Linking
Internal links tell Google which pages matter most.
Key principles:
- Avoid orphan pages
- Link important pages frequently
- Keep key URLs within 3–4 clicks from the homepage
More internal links = higher crawl priority.
8. Monitor and Adjust Using Crawl Data
Crawl budget optimisation is ongoing, not one-time.
Monitor in Google Search Console:
- Crawl requests
- Response times
- Crawl errors
- Host load issues
Use data to fix bottlenecks instead of guessing.
Crawl budget optimisation isn’t about manipulating Google-it’s about efficiency.
When you:
- Reduce URL clutter
- Improve performance
- Focus on high-value content
- Use clean architecture and linking
You naturally help Google discover and rank your pages faster.
For large, ecommerce, or rapidly growing sites, crawl budget SEO can become a quiet but powerful competitive advantage.
FAQs: Crawl Budget SEO
What Is Crawl Budget?
Crawl budget is the number of URLs Googlebot can and wants to crawl on a website within a specific time period.
Why Is Crawl Budget Important for SEO?
If Google doesn’t crawl a page, it can’t index or rank it. Crawl budget optimisation ensures important pages are discovered and evaluated faster.
What Is Google Crawl Budget Based On?
Google crawl budget depends on crawl capacity (server performance) and crawl demand (content quality, links, and freshness).
How to Optimize Crawl Budget Effectively?
You can optimize crawl budget by removing duplicate URLs, improving site speed, cleaning sitemaps, strengthening internal links, and blocking low-value URLs.
What Are Crawl Budget Best Practices for Large Websites?
Key practices include URL consolidation, canonical usage, robots.txt management, accurate status codes, and flat site architecture.
How Does Crawl Budget Optimization Help Ecommerce Sites?
Crawl budget optimization for ecommerce sites prevents Google from wasting crawl resources on filters, variants, and faceted URLs, ensuring product and category pages are prioritised.
How to Help Google Crawl Your Website Faster?
Improve server speed, reduce URL clutter, maintain clean internal linking, and submit accurate sitemaps to guide Google efficiently.